Parent PLUS & Student PLUS Loans: Know Your Options
Very few families can say they’ve been able to save all the money a child will need to complete their college degree. In fact, most students reach their education goals by combining several different funding options. Those include savings, parent contributions, working a part-time job while in school, and different types of financial aid.
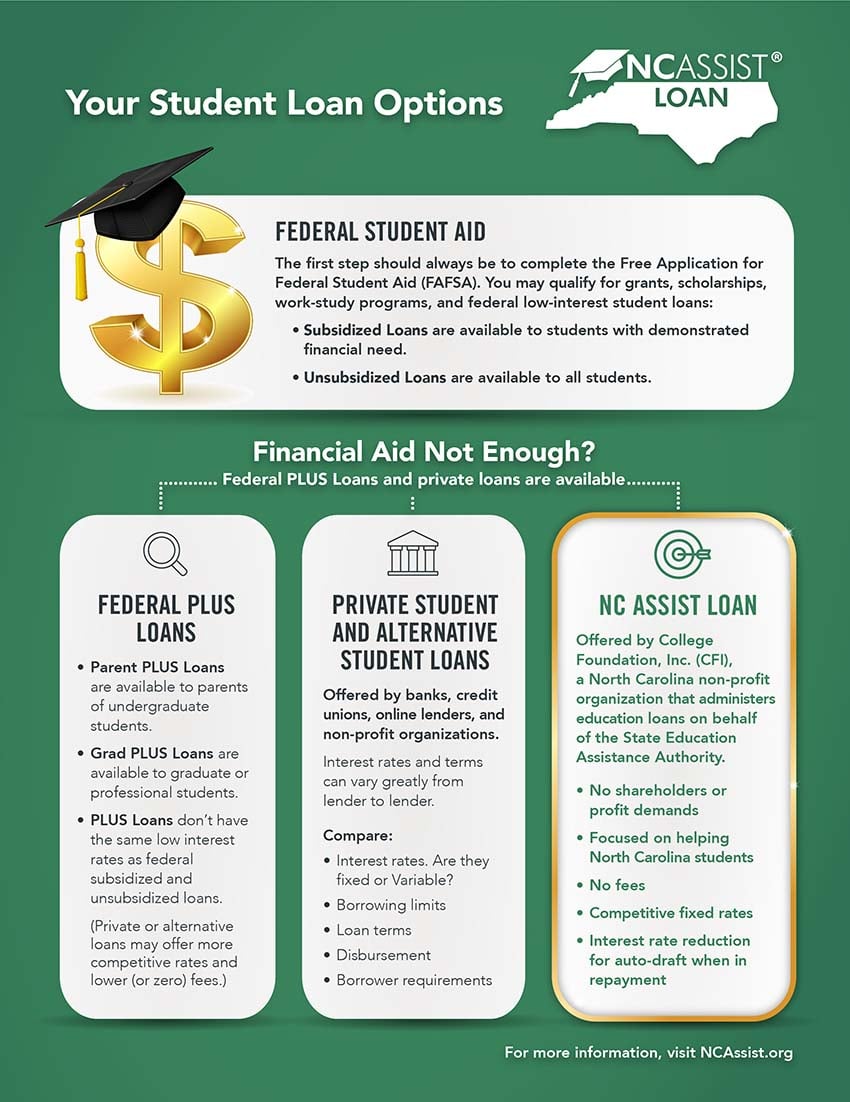
When scholarships and grants aren’t enough to cover the cost of college, students and parents can borrow additional funds from the federal government, private, and nonprofit lenders. This can be a confusing process, so here’s a quick tutorial to explain the options available to students and parents. The first step should always be to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
Financial Aid
You may think that financial aid only means scholarships or grants for students with financial need, but most students will receive some sort of financial aid when they complete the FAFSA. It helps students qualify for grants, scholarships, work-study programs, and federal direct student loans.
Some loans are offered by the U.S. Department of Education to help students reach their higher education goals. Here’s a closer look at federal direct student loans available through the FAFSA:
- Subsidized loans – available to students with demonstrated financial need. The federal government pays the interest while the student is enrolled in school at least half time. The loan limit generally ranges from $3,500 per year for eligible first-year students up to $5,500 per year for eligible fourth-year students.
- Unsubsidized loans – available to all students. While the student is in college, they can pay the interest or allow it to accrue until the repayment period begins. The loan limit for most undergraduate students is $2,000 per year.
When you do the math, a first-year student could receive up to $5,500 in federal direct subsidized and unsubsidized loans. Combined with savings, scholarships, and other state financial aid, this is a good start to pay for college. In fact, financial experts often recommend that students take advantage of all federal subsidized and unsubsidized loans offered through the FAFSA because these types of student loans generally have lower interest rates than PLUS or private loans.
However, these loans charge fees and have borrowing limits. So, if grants, scholarships, and subsidized loans are not enough to cover the cost of college, students and parents have other borrowing options — PLUS Loans and private loans.
Federal PLUS Loans
Parent PLUS and Grad PLUS federal loans are available to parents of undergraduate students and graduate or professional students, respectively. Interest will accrue while the student is in school.
However, just because PLUS Loans come from the federal government doesn’t mean they have the same low interest rates as federal subsidized and unsubsidized loans. So, it’s in the student’s and the parent's best interest to shop around and compare student loan rates. In many cases, a private student loan may offer more competitive rates and fees than a PLUS Loan.
Another point to note — many colleges will add a link in the student’s financial aid award letter or offer to make it convenient for you to apply for a PLUS Loan. This doesn’t mean you have to take advantage of this option, but it’s a good way to start doing your homework if you need additional funds to pay for school. Remember that in many cases, private or alternative loans may have better interest rates and lower (or zero) fees to save students money.
Private Student Loans
The private or alternative student loan market has grown significantly in recent years. These loans are issued by other lenders, such as banks, credit unions, online lenders, and nonprofit organizations, such as College Foundation, Inc. (CFI).
Interest rates and terms can vary greatly from lender to lender, so you’ll need to do some research and go with the loan that meets your needs. You’ll want to consider how much the lender charges in loan fees, whether they offer fixed or variable interest rates, and can you qualify for the loan? For example, NC Assist Loan charges no fees and has lower interest rates than federal PLUS Loans.
NC Assist Loan is offered by CFI, a North Carolina nonprofit organization that administers loans on behalf of the State Education Assistance Authority. This means there are no shareholders or demands to increase profits. The NC Assist Loan is focused on helping students in North Carolina.
Taking advantage of financial aid and doing your homework on the benefits of PLUS and private loans could save you thousands of dollars in fees and interest over the life of the loans. We have additional resources to help you shop for student loans. And when you’re ready, it’s also simple to begin the application process on our website.